- | Home |
- Company |
- Contact |
- News |
- S/ware Eng |
- Standards |
- Academic Support |
- Documents |

- | Requirements |
- Validation |
- RTOS |
- Analysis |
- Software |
- Resources |
- Products |
![]()
Segger J-Link JTAG Debugger
Phaedsys has now closed |

J-Link is a USB powered JTAG emulator for ARM cores. It connects via USB to the Windows (2000/XP) PC host.
Any ARM7/ARM9 core (including thumb mode) and Cortex M3 including SWD supported
Features:
-
USB 2 .0 interface
Download speed up to 720 kbytes/s
-
DCC speed up to 800 kbytes/s
-
Seemless integration into the IAR workbench
-
No power supply required, powered through USB
-
Max. JTAG speed 12 MHz
-
Automatic core recognition
-
Auto speed recognition
-
Support for adaptive clocking
-
All JTAG signals can be monitored, target voltage can be measured
-
Support for multiple devices on scan chain
-
Fully plug and play compatible
-
20-pin standard JTAG connector, optional 14-pin adapter
-
Optional adapter for 5V targets available
-
USB and 20-pin flat cable included
-
Wide target voltage range: 1.2V - 3.3V
-
-
J-Mem (live memory view/edit) included
-
J-Link server (connects to J-Link via TCP/IP) included
-
J-Flash (flash programming software) available
-
Software Developer Kit (SDK) available
-
RDI support available: Use J-Link with any RDI compliant debugger
-
RDI Flash breakpoints available: Unlimited number of breakpoints in flash
-
RDI Flash downloader available: Lets your debugger download into flash
-
Flash programming DLL (Flash SDK) available: Write your own program for flash programming easily
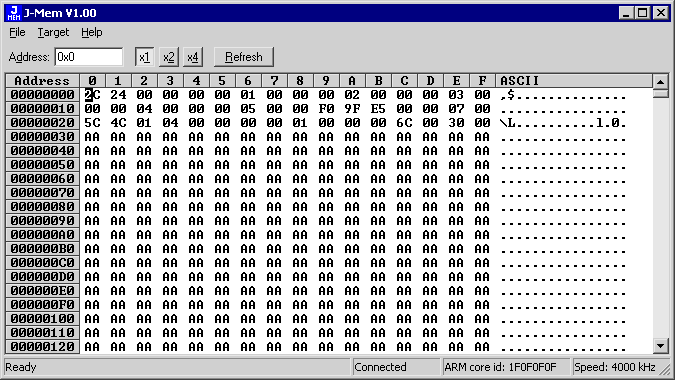
JMEM Memory Viewer
J-Mem is a small (app. 50 kb) stand-alone application for Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP. It requires a J-Link connected to the USB port and an ARM system connected to J-Link via the JTAG interface.
J-Mem displays memory contents of ARM-systems and allows modifications of RAM and sfrs (Special function registers) while target is running. It makes it possible to look into the memory of an ARM chip at run time; RAM can be modified and sfrs can be written. The type of acces for both read and write access can be selected to be 8/16/32 bit.
It works nicely when modifying sfrs, especially because it writes the sfr only after the complete value has been entered.
J-TAG Performance comparison
The following table lists performance values of popular JTAG emulators for download into RAM:
Product |
Download speed |
Abatron BDI2000 |
up to 340 Kbytes/s |
Abatron BDI1000 |
up to 170 Kbytes/s |
Amontec JTAGkey |
up to 135 Kbytes/s |
ARM RealView Multi-ICE |
up to 130 Kbytes/s |
Hitex Tantino |
up to 130 Kbytes/s |
Hitex Tanto |
up to 400 Kbytes/s |
Ronetix PEEDI |
up to 409 Kbytes/s |
Rowley CrossConnect for ARM |
up to 200 Kbytes/s |
Segger J-Link |
up to 720 Kbytes/s |
All download speeds are taken from specifications found on manufacturer's website on March 20, 2007. If different values have been found, the highest one has been used. Please note that the actual speed depends on various factors, such as JTAG, clock speed, host CPU core etc.
Measuring J-Link download speed
JLink.exe has been used to measure performance. The hardware consisted of:
PC with 2.6 GHz Pentium 4, running Win2K
-
USB 2.0 port
-
USB 2.0 hub
-
J-Link
-
Target with ARM7 running at 50 MHz
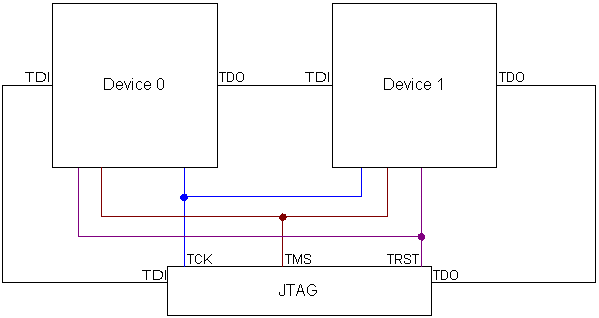
Multiple devices in the scan chain
J-Link ARM can handle multiple devices in the scan chain. This applies to hardware where multiple chips are connected to the same JTAG connector. As can be seen in the drawing below, the TCK and TMS lines of all JTAG device are connected, while the TDI and TDO lines form a bus.
Currently, up to 8 devices in the scan chain are supported. One or more of these devices can be ARM cores; the other devices can be of any other type but need to comply with the JTAG standard.
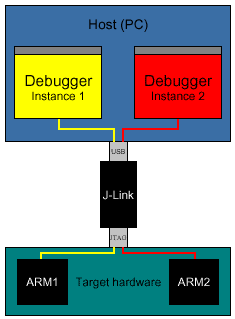
Multi core debugging
J-Link is able to debug multiple cores on one target system connected to the same scan chain.
How multi-core debugging works
Multi-core debugging requires multiple debuggers or multiple instances of the same debugger. Two or more debuggers can use the same J-Link / J-Trace simultaneously. Configuring a debugger to work with a core in a multi-core environment does not require special settings. All that is required is proper setup of the scan chain for each debugger. This enables J-Link / J-Trace to debug more than one core on a target at the same time. Both debuggers share the same physical connection.
Phaedsys has now closed |